CEOs would be wise to insist upon #CyberHygiene intelligent alerting tools
Organisations have invested billions in training users to become its #HumanFirewall and on #CyberSecurity to shore up intrusion defences. However only one in 10 (at best) has a #CyberHygiene solution with intelligent alerting, to measure their defences, and to know the overall risk profile of their digital footprint, or that of the digital supply chain of products services and communications that they engage in, including third parties, which is where the greater risk lies.
CEOs have a responsibility to shareholders to ensure that businesses are able to operate as a going concern. For this to be taken seriously there has to be greater adoption by all companies of the need to monitor their digital health and well-being, to protect reputation and shareholder value.
Differentia Consulting is working with its partners, insurers and security experts, to share such capability. This means that you can monitor and measure your entire Digital Supply Chain in ways that you need. This will be delivered by means of a #CyberHygiene-Dashboard reporting and alerting service, that monitors the scores, security ratings, and the health or wellbeing of supply chains that deliver your products or services. Enhanced services available.
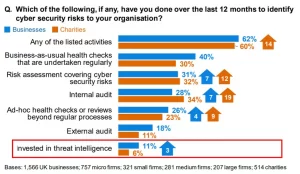
Only 11% of UK companies invest in Cyber security threat intelligence according to survey by UK Gov
Why Use Threat Intelligence tools to Measure the Cyber risk in your Digital Supply Chain?
Big insurers are now hiring global heads of Cyber Insurance to manage the provision of Cyber Insurance cover and take a slice of what is expected to be a $35Billion Insurance market in the next few years. GDPR fines are excluded, as is behaviour as a result of an act of war. By demonstrating that you have taken reasonable steps to manage both your compliance and importantly that of your vendors in the same Digital Supply Chain you should be able to leverage reduced fines and/or improved premiums/payouts. For this, you will need a threat intelligence monitoring and alerting solution.
What is the point of only measuring your levels of compliance?
By using publicly available data we can build a complete picture of the “risk” associated with your whole digital supply chain. ie The end-to-end technology infrastructure and data processing used to distribute goods or services. Similar to how companies are asked to comply with Anti Slavery directives across a supply chain we should be able to see how safe companies are to do business with by looking at cyber health across their supply chain. By doing so can mitigate against the risk of penalties that equate to as much as 4% of group turnover, equating to as much as 50% of annual profit (or more).
Hence only measuring your levels of compliance will not satisfy regulators that you have taken sufficient reasonable measures to manage the risk.
Likewise, before investing in a company we might want to take a view on the whole organisation or group, not just one trading entity. Typically this could include Vendor Risk Management also.
#CyberHygiene KPIs – Why do CEOs need CyberHygiene based KPIs?
- What is a company’s reputation worth?
- How do you protect your reputation?
- Fines of up to 2%+4% ie 6% of Turnover (typically 50%+ of operating profit) require board attention [2% alone for not filing a breach in time]
- Can your business afford disruption and recover without loss?
…questions that insurers exploit to ensure that you take out Cyber Insurance. (Although some fines cannot be insured against).
By monitoring, measuring, and managing by exception you can ensure that your company is always aware of Cyber risks and that it has a plan to ensure that when there are recognised issues that impact the ability for Cyber Compliance you are alerted to take action. Compliance requires behaviour controls security policies and procedures and the need to report breaches.
“By setting #CyberHygiene KPIs the company enables itself to make smarter decisions about its digital security perimeter to reduce risk, protect its reputation, and future.” Adrian Parker Differentia Consulting.
You are 5.4 Times More Likely to be Hacked if your digital footprint does not meet the minimum criteria for a single risk factor.
Whilst the definition of Cyber Hygiene below is primarily focused upon behaviours what is clear is that we now need to expand the definition to look at the; technical, digital and data controls of an organisation. Hence why certifications such as Cyber Essentials are a great start to improving a company’s Cyber Hygiene (Digital Wellbeing). Further, why simply look at one organisation, when typically you do business with a supply chain? Hence the offer to support you in looking at your digital supply chain. You are only as good as your weakest link and according to SecurityScorecard 5.4 times more likely to be subject to a breach if any one part of your supply chain scores below the minimum threshold.
Jamie Dimon says the risk of cyberattacks ‘may be the biggest threat to the US financial system’
Key facts:
J.P. Morgan Chase spends almost $600 million on cyberdefenses, according to CEO Jamie Dimon’s annual letter to shareholders.
“The threat of cyber security may very well be the biggest threat to the U.S. financial system,” Dimon says.
Jamie Dimon, CEO of JP Morgan Chase, speaking at the Business Roundtable CEO Innovation Summit in Washington, D.C. on Dec. 6th, 2018.
Janvhi Bhojwani | CNBC
The current Average cost of a Cyber Security breach is >$8 Million and is likely to increase
“The current average cost incurred by a company in the US that suffers a data breach stands at $8.19 million. Amongst organizations that have implemented fully automated cybersecurity defenses, that cost drops to $2.6 million.” Bernard Marr Excerpt from Forbes post on The 5
biggest Cybersecurity trends in 2020 everyone should know about.
We believe that with regulatory fines this number is going to increase significantly, with the potential for fines from regulatory bodies both national and international. Hence the need to protect the entire Digital Supply Chain.
Who is regulating who?
ICO:
- Ensures Personal Data is being used for the purpose that it was shared and protected at all times.
What Should You Be Monitoring?
Website:
-
Website Malware Scanner
– monitors for signs of website malware and indicators of compromise (IOC)
-
Website Server-Side Scanner
– Penetration testing of server for signs of malware to find backdoors, phishing pages, spam, DDoS scripts etc
-
Blacklist Status
– Blacklisted site can lose 95% of its traffic
-
DNS Status
– Be Alerted when hackers changing your DNS with malicious intent
-
SSL Certificate Monitoring
– receive immediate alerts so you can take action
-
SEO Spam Scanner
– Spam keywords and link injections harm your brand. Discover signs of SEO spam before Google and other search engines do.
-
Website Uptime Monitoring
– Websites can go down. It is critical to know when visitors can’t access your site so that you can take immediate action.
Cyber Hygiene by Industry Sector
Possible areas to cover are
Threat assessments and links to data from external agencies
Attack mitigation
Planning and monitoring
Analytics for command centre staff/operations
Regulatory reporting
Association to critical application and infrastructure endpoints
Software patching across entire infra – desktop, mobile and server ( on-prem and cloud )
Employee training
Employee monitoring
Phishing – both avoiding and monitoring, but running internal tests
Use of enterprise password vaults
Policy management around password controls, privileged access
SDLC best practice adoption around security ( e.g. OWASP Top 10 )
Qlik’s unique associative engine, AI capabilities, NPrinting and Ping augmented alerting add capabilities in this space.
Financial Services
The number 1 threat faced by all financial institutions today is the daily barrage of cyber-attacks from external criminals, state-sponsored attacks and even employees.
The consequences include financial loss, reputational loss and ultimately collapse.
Huge sums of money are spent preventing, analysing and adapting to the evolving threat.
Many FS companies have a large suite of reporting apps in this space
High Tech
High Tech companies which provide subscription-based products and services.
If these company’s security is breached, their customer bases are all at risk.
FMCG
Distribution/Manufacturing who rely and depend on a long supply chain. There will come a time if it doesn’t exist already that suppliers must prove to their customers that they have mitigated against Cyberattack.
What is CyberHygiene?
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) and the Council on Cyber Security (CCS) defines cyber hygiene as a means to appropriately protect and maintain IT systems and devices and implement cyber security best practices.
This risk mitigation technique is a must for all businesses deploying emerging technologies to their networks. Without clear assessments and interventions, hackers will have an easy in through unpatched and outdated solutions, and unforeseen security gaps in newer technologies.
Keeping Good Cyber Hygiene Habits as a Company
While cyber hygiene isn’t ironclad protection, it’s important for everyone in contact with your network, from the CEO to the newest intern, to act securely with these ten tips:
1. Keep an inventory of hardware and software on the company network.
2. Develop a process for software installation by end-users. That could include limiting the installation of trusted software or prohibiting and blocking all installation without prior approval from IT.
3. Educate users on practising good cyber behaviour, including password management, identifying potential phishing efforts, and which devices to connect to the network.
4. Identify vulnerable applications that aren’t in use and disable them.
5. Consistently back up data and keep multiple copies. Consider using a secure cloud solution as well as on-premise.
6. Turn to industry-accepted secure configurations/standards like NIST and CIS Benchmark. These can help organizations define items like password length, encryption, port access, and double authentication.
7. Patch all applications right away–regularly. Unpatched systems are one of the biggest risk factors in attacks.
8. Create complex passwords.
9. Limit the number of users with administrative privileges.
10. Upgrade aging infrastructure and systems.
The #HumanFirewall plays a big part in your #CyberHygiene defences
Good cyber hygiene habits to help you stay safe online (Norton)
Have you heard of something called cyber hygiene? Surely, brushing your teeth and taking showers isn’t something traditionally associated with technology — yet the term is a useful metaphor for needing to make smart decisions about your smart devices.
Good hygiene is something you’re taught as a child and something that generally sticks with you for the rest of your life. It involves three basic principles: using products and tools that fit your hygiene needs, performing these hygienic tasks correctly, and establishing a routine.
But what is cyber hygiene and what does it have to do with your computer and connected devices?
Cyber hygiene is about training yourself to think proactively about your cyber security — as you do with your daily personal hygiene — to resist cyber threats and online security issues. Unfortunately, cyber security still isn’t taken as seriously as cavities and root canals. Some people take cyber security for granted, but this may change, as cyber threats continue to evolve. In the meantime, establishing solid cyber hygiene practices should be as routine as brushing your teeth.
Here are a few tips to get you and your family thinking about good cyber hygiene practices.
Use the right tools for cyber hygiene
Ever try brushing your teeth without a toothbrush? Without the right tools for the job, maintaining personal hygiene would be a bit more difficult, if not impossible. The same is true for managing good cyber hygiene. Without the right products and tools, personal information you think is secure could, in fact, be at risk.
Reputable antivirus and malware software, a network firewall, and password protection all help to protect personal data stored on your home computer. Taken together, these tools may help you feel confident about the security of your home computer, laptop, smartphone, and other devices.
Additionally, you should always make sure the security brand is a reputable source before installing anything on your computer or other devices.
Be thorough, be accurate with cyber hygiene Everyone is supposed to floss, right? But does everyone do it as much as the dentist recommends? Deleted or presumably irretrievable files on your computer require a kind of flossing and demand special attention from time to time.
For example, you may think that regularly emptying the trash can or recycle bin removes personal or sensitive data from the hard drive. This is not the case.
To permanently delete files from your computer, you must use data-wiping software. Whenever you introduce new software, add on hardware, or modify system files, you’re at risk of losing personal data. Get in the habit of regularly clearing out data you don’t need and making sure to wipe it clean from the hard drive.
Another area of security that requires your attention is password protection. Don’t get lazy and skimp on creating complex, unique passwords for each account, using combinations of at least 12 letters, numbers, and special characters. Change your account passwords regularly, and you’ll be on your way to better cyber hygiene in no time.
Make cyber hygiene part of your routine
Learning to monitor your cyber security regularly can increase your chances of avoiding an online threat. But just like any habit you wish to make stick, it requires routine and repetition.
Get started by setting an alarm or marking a calendar with dates to address a series of tasks — things such as scanning for viruses with antivirus software, updating the operating systems of all your devices, checking for security patches, wiping the hard drive, and changing your passwords. Once you begin to get the hang of cyber hygiene, it will become second nature to you.
Key steps for good user cyber hygiene
Good cyber hygiene is a general practice that can help keep you safe and secure online, but there are several best practices to ensure your cyber hygiene is the best it can be. Here are nine essential steps.
1: Install reputable antivirus and malware software
The first and maybe most important step is installing antivirus software. What is it designed to do? Antivirus software is a program or umbrella of programs that scan for and eradicate computer viruses and other malicious software, or malware. It’s a vital component of your overall cyber hygiene in its protection against security breaches, along with other threats.
Specifically, antivirus software provides protection by performing key tasks, including these.
- Pinpointing specific files for the detection of malicious software.
- Scheduling and performing automatic scans.
- Scanning either one particular file or your entire computer, or a flash drive, depending on your specific needs.
- Erasing malicious codes and software.
- Confirming the “health” of your computer and other devices.
2: Use network firewalls
Using a network firewall is another key habit for maintaining good cyber hygiene. Firewalls are a first line of defence in network security by preventing unauthorised users from accessing your websites, mail servers, and other sources of information that can be accessed from the web.
3: Update software regularly
Update your apps, web browsers, and operating systems regularly to ensure you’re working with the latest programs that have eliminated or patched possible glitches. Setting up this feature to update automatically will help ensure you have the latest protections.
These updates are particularly important because they often include software patches. Software developers issue security patches whenever they discover software flaws — flaws that could let in viruses or hackers. Developers may not always alert you when a critical patch has been implemented, because this might give hackers the heads-up, as well. Thus, regular updates will ensure these patches plug any holes in your software.
4: Set strong passwords
Setting strong passwords for all of your devices is essential. Your passwords should be unique and complex, containing at least 12 characters along with numbers, symbols, and capital and lowercase letters. Changing your passwords regularly — and never sharing or reusing the same password — will help prevent hackers from figuring them out.
Additional device controls are firmware passwords. These are hardware passwords that help prevent others from using your computer. While disk encryption prevents cyber thieves from accessing information stored on your device, firmware passwords protect your hardware by preventing your machine from being rebooted or reset without your password.
5: Use multi-factor authentication (Probably the best protection there is)
Two-factor or multi-factor authentication is a best practice that offers an additional layer of protection. Two-factor authentication usually requires you to submit your password and username along with, say, a unique code that is sent to your cell phone. This may be all that is needed for some systems, but multi-factor authentication adds additional layers of security with the use of biometrics, like facial or fingerprint recognition, to make it harder for hackers to gain access to your device and personal information.
6: Employ device encryption
While most companies automatically have data encryption processes in place, you also may want to encrypt your devices and other media that contain sensitive data — including laptops, tablets, smartphones, removable drives, backup tapes, and cloud storage. In fact, many devices use encryption as the default for data stored on smartphones. Some apps are using end-to-end encryption, and other services encrypt data on your devices and back them up in the cloud. Another option is to use an encrypted USB memory stick for protecting sensitive data.
7: Back up regularly
It’s also smart to keep your files secure by backing up important files offline, on an external hard drive, or in the cloud. This can help protect against many types of data loss, especially if hackers gain access to one of your devices.
8: Keep your hard drive clean
If you’re selling your laptop, tablet or smartphone, it’s important to ensure your personal or sensitive information doesn’t get passed along, as well. If your device is hacked, a clean hard drive means less information that’s accessed.
But merely deleting files or data may not be enough. Part of good cyber hygiene is reformatting and then wiping your hard drive clean. For example, if you want to sell your computer and have used it for online banking, you’ll want to consider disk-wiping to remove software and data from your hard drive.
9: Secure your router
Don’t forget to protect your wireless network. This involves turning off and updating the default name and password the router came with from the manufacturer, turning off remote management, and logging out as the administrator once it’s set up. Also, make sure your router offers WPA2 or WPA3 encryption to maintain the highest level of privacy of information sent via your network.
Remember, it’s smart to practice good cyber hygiene habits. If you set up your computer and other devices with reputable antivirus programs, update them regularly, create strong passwords, and keep everything clean, you’ll be on your way to creating cyber habits that may help keep you safe and secure online.

Cyber Security Breaches Survey by UK Government 2019
A survey detailing business and charity action on cyber security and the costs and impacts of cyber breaches and attacks.
Cyber Insurance
Cyber-insurance is an insurance product used to protect businesses and individual users from Internet-based risks, and more generally from risks relating to information technology infrastructure and activities. Risks of this nature are typically excluded from traditional commercial general liability policies or at least are not specifically defined in traditional insurance products. Coverage provided by cyber-insurance policies may include first-party coverage against losses such as data destruction, extortion, theft, hacking, and denial of service attacks; liability coverage indemnifying companies for losses to others caused, for example, by errors and omissions, failure to safeguard data, or defamation; and other benefits including regular security-audit, post-incident public relations and investigative expenses, and criminal reward funds. Source: wikipedia
Cyber insurance market is estimated to grow to a $25 billion industry by 2025 from less than $5 billion currently. Which is arguably low considering that GDPR and similar Personal Information compliance requirements would indicate a need for all companies that do business that includes Personal Data. Of interest is that Cyber Insurance. like most insurance, excludes acts classified as acts as War.
On the positive front Cyber insurance payout rates are at 99%, but uptake is still far too low, according to the Association of British Insurers 89% of businesses are potentially unprotected against attacks.
Cyber insurance payout rates at 99%, but uptake is still far too low
08/08/2019
Up to 89% of businesses potentially unprotected against attacks
The Association of British Insurers has, for the first time, revealed that 99% of claims made (207) on ABI-member cyber insurance policies in 2018 were paid*. This is one of the highest claims acceptance rates across all insurance products.
Despite this, the take-up rate of cyber insurance by businesses in the UK is still worryingly low, with the overall market size estimated at less than a tenth of the size of the UK’s pet insurance market**. Just 11% of businesses are thought to have a specific cyber insurance policy in place, meaning millions of small businesses could be at risk.
The UK has the potential to be a world leader in cyber insurance, but the inability to access raw breach data risks limiting the potential of the market. The ABI has been asking the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) to make anonymised cyber breach data publicly available, which would enable insurers to price risk more accurately and manage exposure more effectively by feeding this data directly into their modelling. Ultimately this would make cyber insurance more widely available, more accurately priced and better tailored to each business.
Unfortunately, the ICO has yet to agree. The ABI will continue to work with the ICO to find a solution that enables both innovation and data privacy in the Cyber market.
James Dalton, the ABI’s Director of General Insurance Policy, commented:
“Cyber insurance is a valuable product – the claims acceptance rates speak for themselves and the additional support a business receives, beyond dealing with the pure financial losses is a key attribute of most cyber insurance policies, too often overlooked.
“Data is key to insurers’ ability to better understand and more accurately price cyber risk. We need the ICO to work with us to find what data can be shared to help insurers provide more cover to the many businesses that need it in this digital age.”
Cyber cover provides extensive services focused on preventing a breach from occurring in the first place, as well as helping with the recovery and management of costs associated with an attack. Recent high-profile cases of cyber breaches have included British Airways and Marriott International, which highlight just how important this type of cover is.
What is the value of cyber insurance?
- Cyber business interruption loss: If a cyber-attack interrupts your business operations, insurers will cover your loss of income during the period of interruption and beyond. This can be a critical safety net as you look to recover your normal working pattern.
- Privacy breach costs: This protection will cover your business for costs arising from dealing with a security breach. For example, notifying customers of a cyber breach, the costs of hiring a call centre to answer customer enquiries, the costs of public relations advice, IT forensic costs, any resulting legal fees and the costs of responding to regulatory bodies.
- Cyber extortion cover: This protects your business from ransomware and other malicious attempts to seize control of your operational or personal data until a fee is paid. This clause will typically provide for a reimbursement of the ransom amount demanded by the attacker as well as any consultant fees to oversee the negotiation.
- Hacker damage: This protects your business from damage inflicted by a hacker on digital assets. In particular, it provides protection against the loss, corruption or alteration of data as well as the misuse of computer programmes and systems.
- Media liability: This protects a business in the event that your digital media presence leads to a party bringing a claim against your business for libel, slander, defamation or the infringement of intellectual property rights. This is especially important for companies that rely on the transmission of digital data via email, a website or a large social media presence.
- Cyber forensic support: This aspect of cover provides for near immediate 24/7 support from cyber specialists recommended by your insurer in the period following a hack or data breach. These specialists are able to assess your systems, identifying the source of any breach and suggest preventative measures for the future.
Source: https://www.abi.org.uk/news/news-articles/2019/08/cyber-insurance-payout-rates-at-99-but-uptake-still-far-too-low/
GDPR fines not insurable in the UK
As companies scramble to be GDPR-ready, with only a week left before the General Data Protection Regulation is enforced, a new guide shows you can’t be covered against fines if you operate in the UK… and, well, pretty much elsewhere.
In fact, of the 30 countries reviewed by Aon and DLA Piper, it turns out such fines are insurable in only two jurisdictions – Finland and Norway. In most countries, the answer seems an outright no, while eight countries are labelled as ‘unclear’.
“In these jurisdictions, specific details around individual cases, for example, the conduct of the insured and whether the fine is classed as criminal, will need to be considered,” said the two firms in a joint announcement when the guide “The price of data security” was released.
These ‘unclear’ countries are the Czech Republic, Estonia, Germany, Greece, Lithuania, the Netherlands, Poland, and Sweden.
“GDPR will expose organisations to significantly higher risks related to how they manage and store personal data,” said Vanessa Leemans, chief commercial officer, Aon cyber solutions EMEA. “Data breaches, and other cyber events, could see businesses face both major fines and extensive costs.
“It is therefore essential that organisations fully understand where their exposures lie. They should work closely with their insurance partners to ensure they have an appropriate risk transfer solution and incident response plan in place.”
Aside from the GDPR penalties, the guide also examined the insurability of costs associated with non-compliance, as well as the insurability of non-GDPR regulatory fines.
“While there are only a few jurisdictions where GDPR fines are insurable, insurance against legal costs and liabilities following a data breach is widely available across Europe and may provide valuable cover to organisations,” said Prakash (PK) Paran, co-chair of the global insurance sector at DLA Piper.
But the law firm partner believes prevention is better. “Corporate groups still need to consider reputational damage and impact on existing customers, the wider market, and their relationships with regulators, all of which may go beyond quantifiable financial losses,” he said.
ICO needs to be informed of a Cyber breach.
What should you do if you suffer a personal data breach? – responding-to-a-cybersecurity-incident.pdf
Free Cyber Resources
 Sucuri Sitecheck – Sucuri offers a Free website security check & malware scanner. Simply enter a URL (eg. yourdomain.com) and the Sucuri SiteCheck scanner will check the website for;
Sucuri Sitecheck – Sucuri offers a Free website security check & malware scanner. Simply enter a URL (eg. yourdomain.com) and the Sucuri SiteCheck scanner will check the website for;
- known malware, viruses, website errors, and malicious code:- Detect malicious code and infected file locations by scanning your external website source code.
- blacklisting status:- See if your website is blacklisted by website security authorities such as Google, Norton, etc.
- security issues:- Check your website for security anomalies, configuration issues, and security recommendations.
- out-of-date software:- Identify if your website is running an outdated CMS or vulnerable plugins and extensions.
Sucuri does advise that remote scanners have limited access and results are not guaranteed
 Security Scorecard Provides insight into various aspects of your Domains over time. They also offer a free lookup Scoring Service. Further SecurityScorecard, recognises that nonprofit organisations fulfil many essential roles in society, yet oftentimes do not have the resources to mitigate risk of cyber attack. SecurityScorecard’s “Project Escher” is dedicated to ensure nonprofits are not obstructed from performing their vital work for the community by provisioning eligible nonprofit organizations with the knowledge and tools that are essential to improving their security posture and defending their cause against critical vulnerabilities.
Security Scorecard Provides insight into various aspects of your Domains over time. They also offer a free lookup Scoring Service. Further SecurityScorecard, recognises that nonprofit organisations fulfil many essential roles in society, yet oftentimes do not have the resources to mitigate risk of cyber attack. SecurityScorecard’s “Project Escher” is dedicated to ensure nonprofits are not obstructed from performing their vital work for the community by provisioning eligible nonprofit organizations with the knowledge and tools that are essential to improving their security posture and defending their cause against critical vulnerabilities.
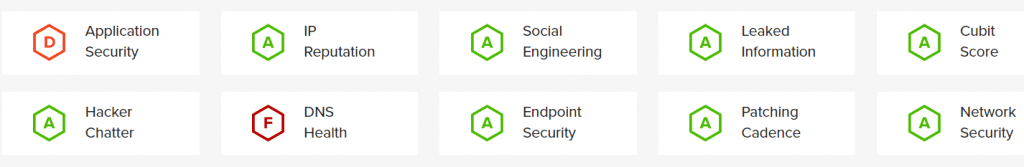
Application Security
Web apps are the engine of the online experience. Boasting cloud storage and dynamic use, web apps have become a part of daily life as people increasingly rely on them for business, productivity, and entertainment.
IP Reputation
Your company’s IP reputation is based on the number of malware signals traced back to your company network. Much like a health report, the more negative signals discovered, the more sick and infectious a network will be (which leads to a lower IP reputation).
Social Engineering
More and more, employees are using their corporate accounts in social networks unrelated to work. Depending on their interactions with social media, employees may unknowingly open up opportunities for hackers to trick them into revealing confidential information.
Leaked Information
Each year, hundreds of millions of passwords are stolen, sold on the criminal underground market, or shared freely via hacker sites. Compromised credentials can provide extra opportunities for hackers to break into corporate accounts due to user password reuse.
Cubit Score
We created the Cubit algorithm to help identify security issues considered to be the best and easiest targets for hackers. This score reflects a range of signals such as exposed domains, bad IPs, and other misconfigurations.
Hacker Chatter
There’s an online forum for everything these days, including hacking. Hacker chatter is exactly what it sounds like: a dynamic and active community that is filled with collaboration, planning, execution, and bragging after a successful hoax.
DNS Health
DNS health is all about the quality and authenticity of the emails that fill your inbox. The Domain Name System (DNS) is critical for identifying mail exchange servers. It is also how we do attribution via email addresses, and not obscure IP addresses.
Endpoint Security
Each time you access your company network remotely – by computer, phone, or tablet – you create an endpoint or a potential point of entry. With the rise of employees using their own devices, endpoint security has grown in complexity and hackers have taken notice.
Patching Cadence
A company’s responsiveness, or lack thereof, to a reported vulnerability can publicly reveal the company’s patching cadence. Companies slower to respond can be easily targeted by hackers.
Network Security
Network security is essential for businesses with large networks that require various types of network access for users and systems. Network security exists to close off as much external access as possible to those not part of the network – hackers, in particular.
Vendor Risk Management
Vendor Risk Management enables Vendor Risk Managers to move measure your whole #DigitalSupplyChain performing point-in-time assessment of a vendor and continuous monitoring. Vendor Risk Managers are able to leverage #CyberHygiene Dashboard grades (SecurityScorecard) to automatically monitor their vendors’ cybersecurity posture and set minimum grade requirements for vendors to maintain. If any vendor’s rating drops below the minimum required, they will be automatically notified to re-mediate their score.
#CyberHygiene Dashboard
Adopting the #Cyberhygiene Dashboard for #DigitalSupplyChains enables CEOs to manage reputation, and IT Service Management and Security Operations teams to automatically monitor the cybersecurity risk/posture of their organisation without any manual effort. When adopted, the service allows your teams to monitor and measure changes in Scorecards at three levels: top-level score, factor-level scores, and issue-level findings.
Or significantly using measures that you consider imperative from a compliance perspective. You can monitor your exposure for example by compliance standard, by country, by region, by IP, by risk etc. Further you can work with your insurers to ensure that what they consider risks to be monitored by exception with alerting as needed.
Together we can make a difference.
Cybersecurity: The Threat
What are the major security risks that can cause loss of profits and/or damage to reputation?
1 Phishing
2 Hacking (Malware)-> Ransomware
3 Non use of detection tools to spot patterns of illicit behaviour
4 IoT device vulnerabilities (the more you have the higher the risk)
5 Non encrypted data, non encrypted (salted) passwords
Article: The 5 Biggest Cybersecurity Trends In 2020 Everyone Should Know About. (Bernard Marr, Forbes)
In this conversation with Cybersecurity expert Prof Kevin Curran of Ulster University, Bernard Marr explores the biggest Cybersecurity trends/threats and how to tackle them.